NETWORK – Globalhealth
Information for doctors

Department of Injection Lipolysis
Information on the standard protocol for injection lipolysis / fat-away injection and membership
Doctor search
If you would like to know which certified doctors in your region offer such treatment, please use our new Google-based doctor search.
Patient information
Attention! This page is aimed exclusively at doctors.
For patients who would like to find out more about the therapies we offer, we have created an area specially tailored to your needs:
To the patient information
Note for doctors
The following information is in no way a substitute for comprehensive hands-on training in injection lipolysis. Treatment can only be carried out safely and efficiently with the theoretical and practical experience imparted at our workshops.
Topic navigation
The specialist area of injection lipolysis is the oldest and at the same time the most extensive specialist area within the Aesthetics Network. In addition to the standard therapy of injection lipolysis, this specialist area also deals with all minimally invasive therapies for the targeted reduction of smaller fat deposits.
The development of the injection lipolysis specialist area
The overarching goal of this department, which was founded in 2003 as NETZWERK Lipolysis, was to develop a standardized treatment protocol for injection lipolysis, also known as fat-away injection, which was still largely unknown at the time. The concept developed was so well received internationally that an early cooperation with the universities of Bochum and Regensburg produced numerous scientific publications on this new minimally invasive treatment approach.
Since then, the department has seen its main task as constantly improving the standard protocol and passing on the knowledge already acquired to licensed doctors.
In addition to the development of our Skin Attitude product range to optimize the aftercare of patients, multiple surveys were conducted on the satisfaction and tolerability of the therapy as well as any complications.
Thanks to this continuous development, injection lipolysis is now not only safer than ever before, we have also been able to significantly expand its effectiveness and application options.
The basics of therapy
Mechanisms of action
Injection lipolysis is a minimally invasive aesthetic therapy for the targeted reduction of small regional fat deposits. For this purpose, the compound developed by us is injected subcutaneously into the affected fatty tissue. The adipocytes are thus dissolved and the fat that escapes is transported to the liver with the help of lipases, where it is broken down by enzymes and then metabolized in the mitochondria to form the energy source adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
The inflammatory reaction triggered by the injection subsequently ensures a natural tightening effect of the skin and the underlying tissue. Unlike other treatment methods, this is not a temporary solution by simply reducing the size of existing fat cells, but by removing them completely.
In contrast to liposuction, injection lipolysis provides a uniform and even slimming of the body silhouette. Injection lipolysis is therefore often carried out after liposuction to even out permanent irregularities.

Active ingredients
The compound used within the department consists mainly of polyenylphosphatidylcholine (PPC for short), a highly purified combination of molecules from the lecithin family, deoxycholic acid (DOC) as a solvent and the preservative benzyl alcohol. The formulation of this prescription-only mixture is based on the drug Lipostabil, which was originally developed for the treatment of fat embolisms.
Studies have repeatedly shown that the dissolved PPC not only reduces the toxicity of deoxycholic acid, but also promotes the metabolization of the released fat.
The mixture in equal parts with a separate vitamin B complex ultimately results in our standard compound, which is the subject of all further training courses on this topic. In special cases, such as the treatment of lipomas, the PPC/DOC mixture can also be injected in pure form.
An optional solution is now also available in the form of the Nano PPC 500, which is manufactured exclusively by Viktoria Apotheke in Saarbrücken. The molecule size of the known PPC was reduced to 40-60 nm and dissolved in glycyrrhizic acid instead of DOC.
The Nano PPC 500 is particularly suitable for smaller fat pads, especially in the facial area.
Standard protocol
The standard protocol taught exclusively at the workshops organized by us first includes a detailed introduction to the mode of action and application of injection lipolysis followed by hands-on training on test subjects organized by us. At the same time, the course also includes essential content such as patient selection, information and optimal aftercare for patients.
If you are interested in one of our CME-certified training courses, you can find upcoming dates on the schedule of our Globalhealth Academy.
Publications
Lipolysis Report
Since 2004, the department has been conducting regular statistical surveys on patient satisfaction and possible complications in order to be able to react to anomalies and further optimize the treatment protocol.
In the last so-called Lipolysis Report, 74,000 individual treatments from a total of 29,889 patients were included in the evaluation.
According to the survey, 90% of patients stated that they were satisfied or very satisfied with the facial treatments they had received, while the figure for body treatments was 85%.
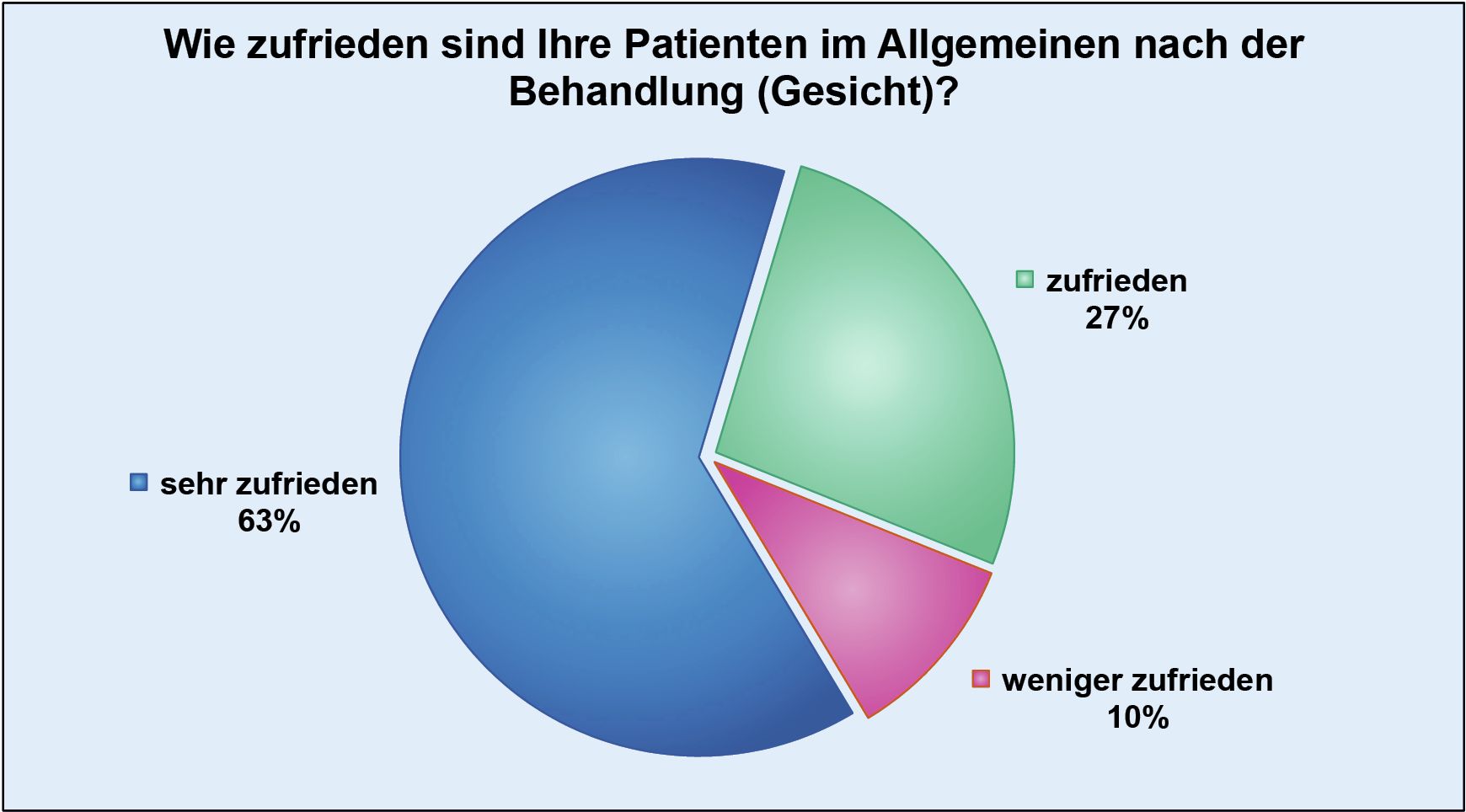
The entire department team is very proud of these results and is constantly working to increase patient satisfaction even further.
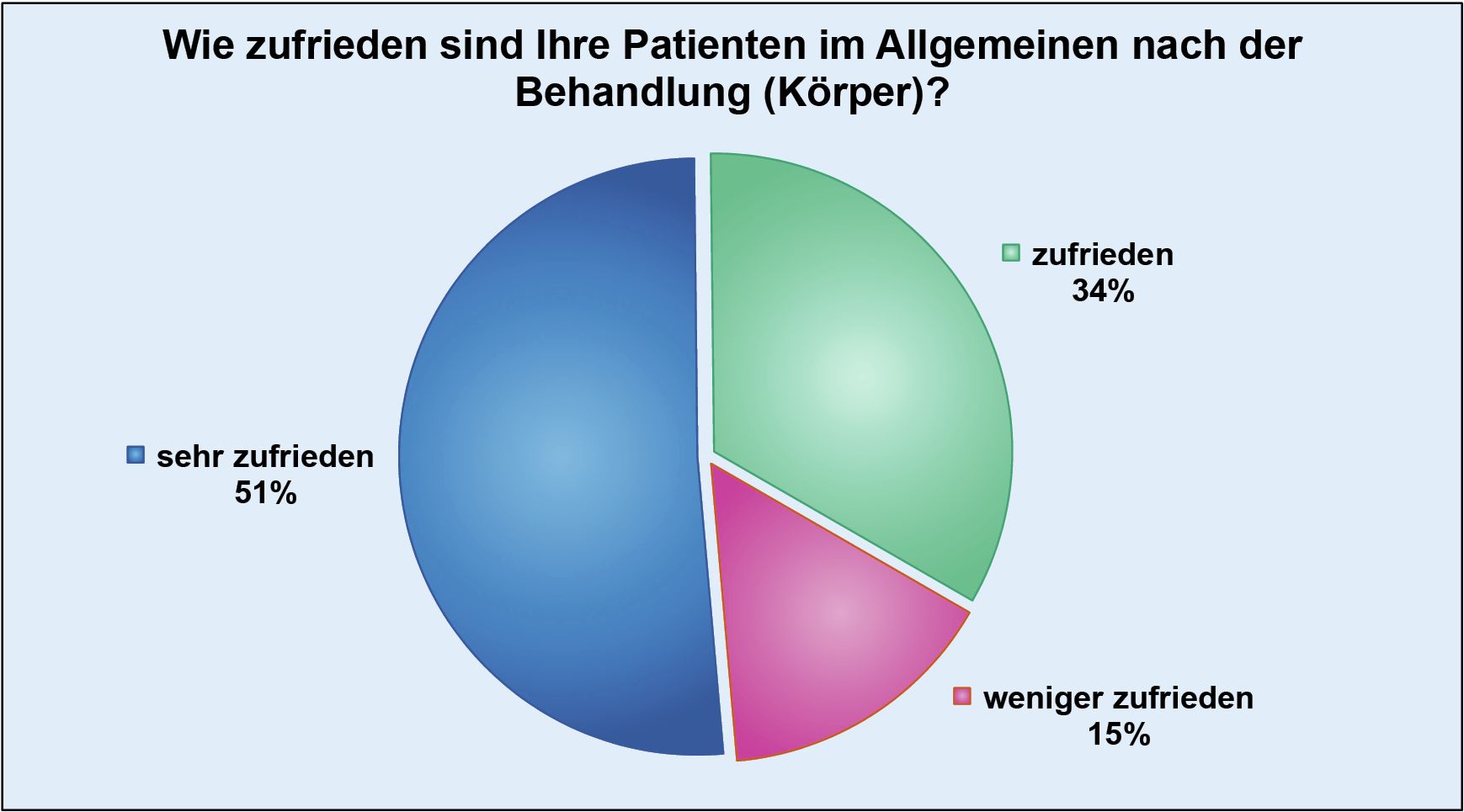
Thanks to the high standards we apply to the implementation of injection lipolysis therapy, we have also been able to reduce the number of possible complications to a minimum.
Necrosis occurred in just 0.1 per thousand (0.01%) of patients, which in individual cases could actually be attributed to a lack of care on the part of those affected during aftercare. The value of documented abscesses is almost identically low at 0.2 per thousand (0.02%).
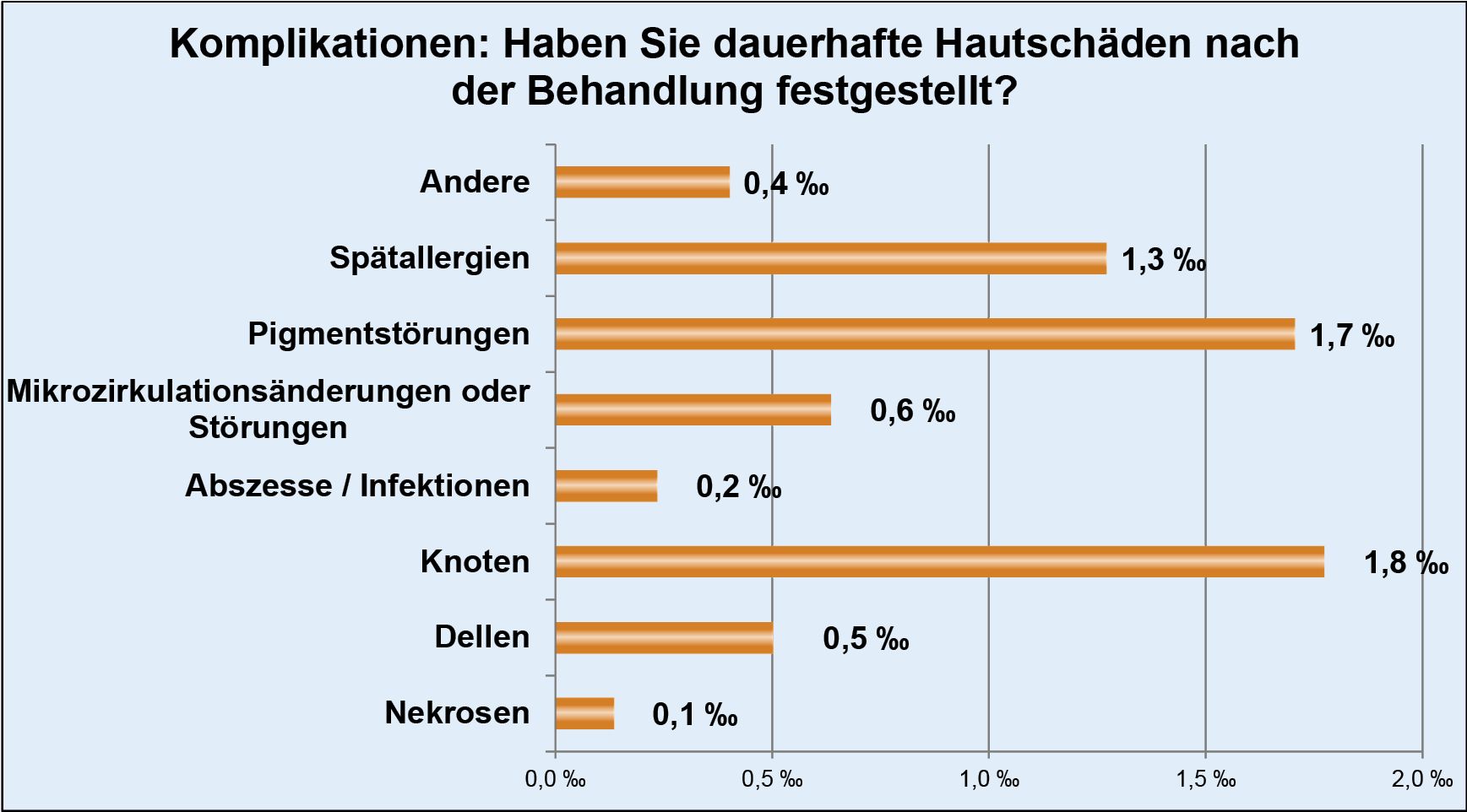
However, since every single complication, whether reversible or not, is still one too many, we attach great importance to sensitizing our doctors to the need for detailed and clear information in patient consultations.
Bibliography
If you would like to familiarize yourself with the subject matter in advance of one of our CME-certified training courses, we have taken the liberty of compiling a detailed literature list on injection lipolysis.
nur Publikationen, die das Thema Injektions-Lipolyse behandeln
Ablon G, Rotunda AM: Treatment of lower eyelid fat pads using phosphatidylcholine: clinical trial and review. Dermatol. Surg. 2004; 30: 422-7
Adelson H: Management of side effects and adverse reactions from injection of phosphatidylcholine. Am. J. Mesotherapy 2006; 5: 16-7
Atiyeh BS, Ibrahim AE, Dibo SA: Cosmetic mesotherapy between scientific evidence, science fiction, and lucrative business. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2008; 32: 842-9
Avelar JM: Comment on “refinement of technique in injection lipolysis based on scientific studies and clinical evaluations”. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2009; 36: 211-3
Bates B: ‘Fat dissolving’ substance injects CCs of controvery: despite growing U.S. interest, Lipostabil’s safety remains uncertain, experts warn. Skin & Allergy News 2003; 34: 1
Baumann L: Cosmeceutical critique: phosphatidylcholine. Skin & Allergy News 2003; 34: 24-5
Bechara FG, Mannherz HG, Jacob M, Mazur AJ, et al: Induction of fat cell necrosis in human fat tissue after treatment with phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate. JEADV 2012; 26: 180-5
Bechara FG, Georgas D, Sand M, Tomi N, et al: Incapsulated fat necrosis after lipolysis of the calf with phosphatidylcholine. Dermatology 2008; 216: 180-1
Bechara FG, Skrygan M, Kreuter A, Altmeyer P, et al: Cytokine mRNA levels in human fat tissue after injection lipolysis with phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate. Arch. Dermatol. 2008; 300: 455-9
Bechara FG, Sand M, Hoffmann K, Sand D, et al: Fat tissue after lipolysis of lipomas: a histopathological and immunohistochemical study. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2007; 34: 552-7
Bechara FG, Sand M, Sand D, Rooterdam S, et al: Lipolysis of lipomas in patients with familial multiple lipomatosis: an ultrasonography-controlled trial. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2006; 10: 155-9
Bechara FG, Sand M, Altmeyer P, Hoffmann K: Intralesional lipolysis with phosphatidylcholine for the treatment of lipomas: pilot study. Arch. Dermatol. 2006; 142: 1069-70
Bellman B: Phosphatidylcholine reaction. Skin & Allergy News 2003; 34: 12
Brown SA: Commentary on: Metabolic and structural effects of phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate injections on subcutaneous fat: a randomized, controlled trial. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2013; 33: 409-10
Brown SA: The science of mesotherapy: chemical anarchy. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2006; 26: 95-8
Bryant R: Controversial mesotherapy: could it be the next botox? Dermatol. Times 2004; 25: 1
Chase CC: Common complications and adverse reactions in a mesotherapy practice. Am. J. Mesotherapy 2006; 1: 14-5
Chung SJ, Chung HL, Ho SL, Sung TK, et al: The role of phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholic acid in inflammation. Life Sci. 2014, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2014.05.013
Co AC, Abad-Casintahan MF, Espinoza-Thaebtharm A: Submental fat reduction by mesotherapy using phosphatidylcholine alone vs. phosphatidylcholine and organic silicium: a pilot study. J. Cosm. Dermatol. 2007; 6: 250-7
De Paula Mesquita T, de Almeida HL, de Paula Mesquita MC: Histological resolution of naevus lipomatosus superficialis with intralesional phosphatidylcholine. JEADV 2009; 23: 714-5
Dobrodin A: The treatment for eye pads revealed. Am. J. Mesotherapy 2006; 1: 16-7
Doerr TD: Lipoplasty of the face and neck. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007; 15: 228-32
Duncan DI: Commentary on: Metabolic and structural effects of phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate injections on subcutaneous fat: a randomized, controlled trial. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2013 33: 411-3
Duncan DI: Letter to the editor – Response to “injection lipolysis with phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate”. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2013; 33: 1073-5
Duncan D, Rotunda AM: Injectable therapies for localized fat loss: state of the art. Clin. PLast. Surg. 2011; 38: 489-501, vii
Duncan D, Rubin JP, Golitz L, Badylak S, et al: Refinement of technique in injection lipolysis based on scientific studies and clinical evaluation. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2009; 36: 195-209,v-vi; discussion 211-3
Duncan DI, Palmer M: Fat reduction using phosphatidylcholine/sodium deoxycholate injections: standard of practice. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2008; 32: 858-72
Duncan DI: The role of phosphatidylcholine in non-surgical body contouring. In: Aesthetic Mesotherapy and Injection Lipolysis in Clinical Practice, edt. by Sh.Madhère. Replika press Pvt, Ltd./India 2007: chapter 8: 61-75
Duncan DI, Chubaty R: Clinical safety data and standards of practice for injection lipolysis: a retrospective study. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2006; 26: 575-85
Duncan DI, Hasengschwandtner F: Lipodissolve for subcutaneous fat reduction and skin retraction. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2005; 25: 530-43
Friedland JA: Comment on “mesotherapy and injection lipolysis”. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2009; 36: 193
Frisari P, Pinto R: Mesosculpt with phosphatidylcholine. Am. J. Mesotherapy 2006; 6: 9
Fritz K, Tiplica G-S: Kosmet. Med. 2011; 32: 280-6
Göller A: Lipolyse in der plastischen Chirurgie. Dissertation, Ulm 2011
Gupta A, Lobocki C, Singh S, Robertson M, et al: Actions and comparative efficacy of phosphatidylcholine formulation and isolated sodium deoxycholate for different cell types. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2009; 33: 346-52
Hasegawa T, Matsukura T, Ikeda S: Mesotherapy for benign symmetric lipomatosis. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2010; 34: 153-6
Hasengschwandtner F, Gundermann K: Injection lipolysis with phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2013; 33: 1071-2
Hasengschwandtner F: Statistische Auswertung einer Befragung der Ärzte des NETZWERK-Lipolyse. Kosmet. Med. 2013; 34: 29-30
Hasengschwandtner F, List P, Spannbauer M: Objektive Messung der Körperzusammensetzung nach Injektionslipolyse mit Polyenylphosphatidylcholin mittels DEXA-Methode (Dual-Energy X-Ray-Absorptiometrie). Kosmet. Med. 2010; #5: 246-52
Hasengschwandtner F: Fat melting injections – The latest scientific findings, terms and methods. Kosmet. Med. 2009; #2: 10-5
Hasengschwandtner F, Brandl D: Phosphatidylcholine. NETWORK-Lipolysis, 2009, http://www.network-lipolysis.com/index.php?id=1513
Hasengschwandtner F: Injection lipolysis: a new method of body contouring. In: Handbook of Cosmetic Skin Care – 2nd Edition, e3dt. By A.Shai, H.I.Maibach, R.Baran, Repikla press Pvt Ltd./India, 2009; chapter 13: pp. 102-5
Hasengschwandtner F: Altersbedingte Fettgewebsveränderungen: Lipolyse, Cellulitebehandlung. In: Hautalterung – Grundlagen, Prävention, Therapie, edt. By
J.Krutmann, T.Diepgen and C.Billmann-Krutmann, Springer press, Heidelberg 2008, chapter 10: pp. 151-165
Hasengschwandtner F, Furtmueller F, Spanbauer M, Silye R: Detailed documentation of one lipolysis treatment: blood values, histology, and ultrasound findings. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2007; 27: 204-11
Hasengschwandtner F: Injection lipolysis for effective reduction of localized fat in place of minor surgical lipoplasty. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2006; 26: 125-30
Hasengschwandtner F: Fat melting injections. Am. J. Mesotherapy 2006; 6: 24-25
Hasengschwandtner F: The subcutaneous injection of phosphatidylcholine for means of lipolysis. Lipodissolve – The non surgical liposculpture. Akt. Dermatol. 2005; 31: 549-52
Hasengschwandtner F: Phosphatidylcholine treatment to induce lipolysis. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2005; 4: 308-13
Heinrich K-G: Efficacy of injection of phosphatidylcholine into fat deposits – a non-surgical alternative to liposuction in body-contouring. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2005; 38: 119-22
Heinrich KG: Injection lipolysis with phosphatidylcholine. Cosmet. Med. 2004; #5-6: 238-40
Hexsel DM, Serra M, de Oliveira Dal’Forno T, Zechmeister do Prado D: Cosmetic uses of injectable phosphatidylcholine on the face. Otolaryng. Clin. N. Am. 2005; 38: 1119-29
Hexsel D, Serra M, Mazzuco R, de Oliveira Dal’Forno T, et al: Phosphatidylcholine in the treatment of localized fat. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2003; 2: 511-8
Hoffmann K: Injection lipolysis. Hautarzt 2010; 61: 847-55
Hoffmann K, Altmeyer P: Verfahren zur Körperformung. In: Ästhetische und plastische Operationen in der Dermatologie, W3L-press/Herdecke/Witten, 2007; chapter 6.1-6.3
Hui KC: Body contouring by liposculpture. The Hong Kong Medical Diary 2008; 13: 20-3
Hübner N-F, Horch RE, Polykandriotis E, Rau TT, Dragu A: A histopathologic and immunohistochemical study on liquification of human adipose tissue ex vivo. Aesth. Plast. Surg. 2014; 38: 976-84
Hübner NF: Adipocytolyse durch Lipostabil®: Ex vivo Untersuchungen an humane Gewebe (Adipocytolysis by Lipostabil® ex vivo investigations with human tissue). Dissertation July 11, 2012
Hunstad JP, De Souza M: Review of “the lipodissolve technique: clinical experience” and author’s comment. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2009; 36: 223-6
Hunter NS, El Tawdy AM, Hegazy RA, El Samanoudy SI, et al: Letter: A 15-patient pilot trial of lipolysis of the hips and thighs using a phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate formulation. Dermatol. Surg. 2013; 39: 791-4
Janke J, Engeli S, Gorzelniak K, Luft FC: Compounds used for ‘injection’ lipolysis destroy adipocytes and other cells found in adipose tissue. Obes. Facts 2009; 2: 36-9
Kardorff B, Gansel RW, Tats R, Balzer L, et al: 2004 Lipodissolve Clinical Report http://www.asal-meso.com/html/news/june_1B_2005_news.htm
Karolchyk S, Seibert L: Detergent effects of sodium deoxycholate are a major feature of an Injectable phosphatidylcholine formulation used for localized fat dissolution: a review. Am. J. Mesotherapy 2006; 1: 18-9
Kato M, Watanabe T, Yamada N, Yoshida Y, et al: Mixed cell granulomatous panniculitis on the cheek due to injection of a solution containing phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate. Dermatol. Surg. 2010; 36: 1779-81
Khan MH, Victor F, Rao B, Sadick NS: Treatment of cellulite – Part II. Advances and controversies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010; 62: 373-384
Kim HS, Park YM, Kim HO, Lee JY: Intralesional phosphatidylcholine and sodium deoxycholate: a possible treatment option for nevus lipomatosus superficialis. Ped. Dermatol. 2012; 29: 119-21
Kirn TF: Injection lipolysis is both defended, criticized: ‘we’ve been using injection lipolysis in my clinic for 2 years now and getting excellent results’. Skin & Allergy News 03/01/08
Klein SM, Schreml S, Nerlich M, Prantl L: In vitro studies investigating the effect of subcutaneous phosphatidylcholine injections in the 3T3-L1 adipocyte model: lipolysis or lipid dissolution? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009; 124: 419-27
Klein SM, Prantl L, Berner A, Schreml S, et al: A new method to quantify the effect after subcutaneous injection of lipolytic substances. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2008; 32: 667-72; discussion 673-4
Kopera D, Horejsi R, Werner S, Moeller R: Injektionslipolyse zur Reduktion von seitlich im Bereich des Trochanters gelegenen Fettdepots („Reithosen”) – kontrollierte Halbseiten-Pilotstudie. JDDG 2008; 6: 287-291
Kopera D, Binder B, Toplak H, Kerl H, et al: Histopathologic changes after intralesional application of phosphatidylcholine for lipoma reduction – report of a case. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2006; 28: 331-3
Kopera D, Binder B, Toplak H: Intralesional lipolysis with phosphatidylcholine for the treatment of lipomas: pilot study. Arch. Dermatol. 2006; 142: 395-6
Kutlubay Z: Evaluation of mesotherapeutic injections of three different combinations of lipolytic agents for body contouring. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2011; 13: 142-53
Kyong YY, Choi KH: Woman with hemorrhagic spots on her abdomen. Clin. Toxicol. 2013; 51: 804-5
Le Coz J, Rittes PG: Guidelines and limitations on the use of phosphatidylcholine (Lipostabil) in mesotherapy. Am. J. Mesotherapy 2006; 2: 6-7
Levy SLJ: Tratamiento de la adiposidad localizada con fosfatidilcolina subcutánea a diferentes concentraciones. Una evaluación histological de su efecto. Dissertation, Mexico October 2013
Li H, Lee J-H, Kim SY, Yun H-Y: Phosphatidylcholine induces apoptosis of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Biomed. Sci. 2011; 18: 91
Madhère S: Mesotherapy in the management of cellulite. In: Aesthetic Mesotherapy and Injection Lipolysis in Clinical Practice, edt. by S.Madhère, Informa Healthcare Replika press Pvt Ltd./India 2007; chapter 10: 85-98
Mahmud K, Crutchfield CE: Lipodissolve for body sculpting - safety, effectiveness, and patient satisfaction. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2012; 5: 16-9
Maggiori S: Traitement mésothérapique des xanthelasmas à la phosphatidilcoline polyinsaturée. 5th Cong. Int. Mésothérapie, Paris/France 1988, Oct.07-09, p.364
Mann MW, Palm MD, Sengelmann RD: New advances in liposuction technology. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2008; 27: 72-82
Matarasso A, Pfeifer TM: Mesotherapy and injection lipolysis. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2009; 36: 181-92
Matarasso A, Pfeifer TM, and the Plastic Surgery Educational Foundation DATA Committee: Mesotherapy for body contouring. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005; 115: 1420-4
McNamara D: Lipolysis melts away appearance of double chin. Skin & Allergy News 04/01/09
McNamara D: Data validate some lipolysis, but not mesotherapy. Skin & Allergy News 2006; 37: 20
McNamara D: Mesotherapy gaining ground as surgery-free fat reducer. Skin & Allergy News 2005; 36: 17
Meißner T: Spritze rückt Fettpolstern und Lipomen zu Leibe. Ärzte Zeitung 04.03.2011
Mokosch A, Mota R, Gerber PA, Homey B: Severe toxic dermatitis after injection lipolysis. Der Hautarzt 2012; 63: 282-5
Môle B: A five years experience of subcutaneous chemical lipolysis with phosphatidylcholine injections. Ann. Chir. PLast. Esthét. 2011; 56: 112-9
Motolese P: Phospholipids do not have lipolytic activity. A critical review. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2008; 10: 114-8
Myers P: The cosmetic use of phosphatidylcholine in the treatment of localized fat deposits. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2006; 19: 416-20
Nanda S: Treatment of lipomas by injection lipolysis. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2011; 4: 135-7
Noh Y, Heo C-Y: The effect of phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate compound injections to the localized adipose tissue: an experimental study with a murine model. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2012; 39: 452-6
Noreldin AA, Abd Elhamid AM, Hashem AM, Afifi AM: A pilot study on the use of injection lipolysis in visceral adipose tissues. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2013 33: 431-5
Olbertz F-W: Injektionslipolyse – ein Erfahrungsbericht nach einjähriger Anwendung. Frauenarzt 2007; 48: 576-7
Ono S, Hyakusoka H: Complications after self-injection of hyaluronic acid and phosphatidylcholine for aesthetic purposes. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2010; 30: 442-7
Palmer M, Curran J, Bowler P: Clinical experience and safety using phosphatidylcholine injections for the localized reduction of subcutaneous fat: a multicentre, retrospective UK study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2006; 5: 218-26
Palumbo P, Melchiorre E, La Torre C, Miconi G, et al: Effects of phosphatidylcholine and sodium deoxycholate on human primary adipocytes and fresh human adipose tissue. Int. J. Immunopath. Pharmacol. 2010; 23: 481-9. Erratum 2010; 23: 970
Park E-J, Kim H-S, Kim M, Oh H-J: Histological changes after treatment for localized fat deposits with phosphatidylcholine and sodium deoxycholate. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2013; 12: 240-3
Peckitt N: Evidenced Based Practice: Phosphatidylcholine – A Review of Evidence for the Mode of Action in Injection Lipolysis. Jeremy Mills Publishing Ltd., Huddersfield, UK, 2005, ISBN: 9781905217137
Pindur L, Sand M, Altmeyer P, Bechara FG: Recurrent growth of lipomas after previous treatment with phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2011; 13: 95-6
Rallis E, Kintzoglou S, Moussatoo V, Riga P: Mesotherapy-induced urticaria – Letter to the Editor. Dermatolo. Surg. 2010; 36: 1355-7
Reeds DN, Mohammed S, Klein S, Boswell CB, et al: Metabolic and structural effects of phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate injections on subcutaneous fat: a randomized, controlled trial. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2013; 33: 400-8. Comments by Brown SA: Aesthet. Surg. J. 2013; 33: 409-10 & Duncan D: Aesthet. Surg. J. 2013; 33: 411-3
Rein P: Injektionslipolyse mit Phosphatidylcholin – Erfahrungen mit der „Fett-Weg-Spritze“. Der Deutsche Dermatologe 2006; #9: 619-20
Rey JW, Schreiner O, Barreiros AP, Heise M, et al: Z. Gastroenterol. 2011; 49: 340-3
Rha EY, Kang JA, Lee JH, Oh DY, et al: Comparative analysis about the effect of isolated phosphatidylcholine and sodium deoxycholate for the viability of adipocyte. J. Korean Soc. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010; 37: 531-4
Rittes PG, Rittes C: Treatment of aging neck with „Lipostabil“ endovena. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2009; 8: 937-9
Rittes PG: The lipodissolve technique: clinical experience. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2009; 36: 215-21
Rittes PG: Non-surgical body contouring: the Brazilian experience. In: Aesthetic Mesotherapy and Injection Lipolysis in Clinical Practice, edt. by Sh.Madhère, Replika press, Pvt. Ltd./India 2007; chapter 9, pp. 77-83
Rittes PG: Complications of Lipostabil endovena for treating localized fat deposits. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2007; 27: 146-9
Rittes PG, Rittes J, Amary MFC: Injection of phosphatidylcholine in fat tissue: experimental study of local action in rabbits. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2006; 30: 474-8
Rittes PG: The use of phosphatidylcholine for correction of localized fat deposits. Am. J. Mesotherapy 2006; 2: 8-11
Rittes PG: The use of phosphatidylcholine for correction of localized fat deposits. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2003; 27: 315-8
Rittes PG: The use of phosphatidylcholine for correction of lower lid bulging due to prominent fat pads. Dermatol. Surg. 2001; 27: 391-2
Rose PT, Morgan M: Histological changes associated with mesotherapy for fat dissolution. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2005; 7: 17-9
Rotunda AM: Injectable treatments for adipose tissue: terminology, mechanism, and tissue injection. Lasers Surg. Med. 2009; 41: 714-20
Rotunda AM: Injectable treatments for adipose tissue: terminology, mechanism, and tissue interaction. Lasers Surg. Med. 2009; 41: 714-20
Rotunda AM, Weiss SR, Rivkin LS: Randomized double-blind clinical trial of subcutaneously injected deoxycholate versus a phosphatidylcholine-deoxycholate combination for the reduction of submental fat. Dermatol. Surg. 2009; 35: 792-803
Rotunda A: Scientific studies aim to dispel controversy surrounding injection lipolysis. The European Aesthetic Guide Autumn 2008, 74 – 84
Rotunda AM: Scientific studies aim to dispel controversy surrounding injection lipolysis. The European Aesthetic Guide, Autumn 2008; 76-84; www.euroabg.com
Rotunda AM: Mesotherapy and injection lipolysis. In: Facial Rejuvenation – A Total Approach, edt. by D.J.Goldberg, Springer press Berlin Heidelberg 2007; chapter 7: 147-65
Rotunda AM, Kolodney MS: Mesotherapy and phosphatidylcholine injections: historical classification and review. Dermatol. Surg. 2006; 32: 465-80
Rotunda AM, Ablon G, Kolodney MS: Lipomas treated with subcutaneous deoxycholate injections. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005; 53: 973-8
Rotunda AM, Avram MM, Avram AS: Cellulite: Is there a role for injectables? J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2005; 7: 147-54
Rotunda AM, Suzuki H, Moy RL, Kolodney MS: Detergent effects of sodium deoxycholate are a major feature of an injectable phosphatidylcholine formulation used for localized fat dissolution. Dermatol. Surg. 2004; 30: 1001-8
Salles AG, Valler CS, Ferreira MC: Histologic response to injected phosphatidylcholine in fat tissue: experimental study in a new rabbit model. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2006; 30: 479-84
Salti G, Ghersetich I, Tantussi F, Bovani B et al: Phosphatidylcholine and sodium deoxycholate in the treatment of localized fat: a double-blind, randomized study. Dermatol. Surg. 2008; 34: 60-6
Salti G, Rauso R: Comments on “Injection Lipolysis with phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate”. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2014; 34: 639-40
Schuller-Petrovic S, Wölkart G, Höfler G, Neuhold N, et al: Tissue-toxic effects of phosphatidylcholine/deoxycholate after subcutaneous injection for fat dissolution in rats and a human volunteer. Dermatol. Surg. 2008; 34: 529-43
Sobel HD: Editorial – Off-label usage of medical devices. Int. J. Cosm. Surg. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2002; 4: 259
Steinert M: Injektionslipolyse. DERMAforum 2009; #1: 4
Strahan JE, Cohen JL, Chorny JA: Granuloma annulare as a complication of mesotherapy: a case report. Dermatol. Surg. 2008; 34: 836-8
Tanner B, Barabas T, Crook D, Link C: A future for injection lipolysis. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2013; 33: 456-7
Tausch I, Kruglikov I (2015) The benefit of dualfrequency ultrasound in patients treated by injection lipolysis, journal of clinical and aesthetic. Dermatology(Basel) 8(8):42–46
Tawfik HA, Zuel-Fakkar NMA, Wlmarasy R, Talib N, et al: Phosphatidylcholine for the treatment of prominent lower eyelid fat pads: a pilot study. Ophthal. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011; 27: 147-51
Toledo LS: a) Preface b) Emerging techniques in aesthetic plastic surgery. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2009; 36: a) xi-xiii b) 177-80
Treacy PJ, Goldberg DJ: Use of phosphatidylcholine for the correction of lower lid bulging due to prominent fad pads. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2006; 8: 129-32
Uygur F, Evinç R, Duman H: Is phosphatidylcholine harmful to the peripheral neural tissue? An experimental study in rats. Aesthet. J. Surg. 2008; 28: 663-7
Walsh N: Some would halt lipolysis Tx pending safety data. Skin & Allergy News 2004; 35: 26
Weidmann M, Lettko M, Prantl L (2016) Injektionslipolyse, J .Ästhet Chir DOI 10.1007/s12631-016-0047-2
Weiss DD, Carraway JH: Eyelid rejuvenation: a marriage of old and new. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005; 13: 248-54
Witort EJ, Pattarino J, Romano FM, Dini M, et al: Lipolytic effectiveness of phosphatidylcholine in the treatment of ‘buffalo hump’ of HIV patients. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2011; 64: e26-8
Won TJ, Nam Y, Lee HS, Chung S, et al: Injection of phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholic acid regulates gene expression of lipolysis-related factors, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and hormones on mouse fat tissue. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013; 60: 263-8
Wong GR, Chen W-P: Phosphatidylcholine/deoxycholate lipolysis and hyaluronic acid augmentation to enhance nonsurgical lower facial contouring using botulinum toxin type A. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2011; 10: 159-62
Worcester S: Lipodissolve mesotherapy is gaining popularity. Skin & Allergy News 2007; 38: 25
Young VL: Letter to the editor – Response to “injection lipolysis with phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholate”. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2013; 33: 1076
Young VL: Lipostabil: the effect of phosphatidylcholine on subcutaneous fat. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2003; 23: 413-7
Zhang Y, Gao J-h, Jiang P, Wang L-y, et al: Chin. J. Aesthet. Med. 2006; 15: 1346-8